The root of a number is that number which, when multiplied by itself so many times, equals the given number; the 'square' root of 4 is 2, ie 2 X 2 = 4, and this is written thus
![]()
Similarly the 'cube' root of 8 is 2, ie 2 x 2 x 2 = 8, and ![]() etc. Note the little 2 in the sign for square root is normally omitted so that
√ signifies the square root.
etc. Note the little 2 in the sign for square root is normally omitted so that
√ signifies the square root.
![]()
The following should be memorised as they can prove to be very useful
![]()
For example
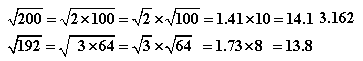
It is always worth checking to see if the number left after dividing by 2, 3 or 5 is a perfect square.
The square root of a number expressed in the index notation is found by dividing the index by 2, thus √106 = 103 and √1012 = 106 and so on. Similarly √10-6 = 10-3 etc. Should the index be an odd number, it must be made into an even number as follows.

The constant term π occurs in many calculations has great significance in mathematics and is the ratio of the circumference to the diameter of a circle. π can be taken to be 3.14 or 22/7. The error in taking π2 as 10 is less than 1.5% and is acceptable here. 1/π can be taken as 0.32 and 1/2π can be taken as 0.16 (The error is calling this 1/6 is too high and should be avoided). The 1/2π = 0.16 is particularly useful to remember as the constant 1/2π is common in electronics.