
A discrete component having the property of resistance is called a 'resistor'.

Photo 2.1 A selection of commonly found resistors types
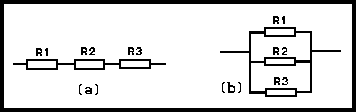
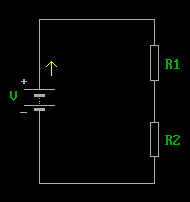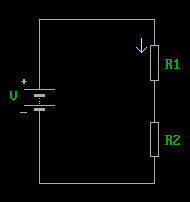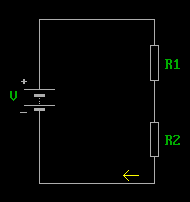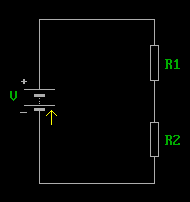

Fig 2.2. Resistors (a) in series, and (b) in parallel
In Series A number of these can be connected as shown in Fig 2.2(a) and in above the animation. This is known as the 'series' connection and the effective resistance, R, is:
![]()
In parallel The 'parallel' connection is shown in Fig 2.2(b) and the above animation. The effective resistance in this case is:
![]() or
or
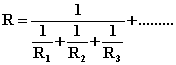
The effective resistance of only two resistors in parallel is:
![]()
The commonest forms of resistor are:
They are graded according to their 'dissipation', ie the amount of heat they can dissipate safely for a given temperature rise. Generally the larger the component, the more surplus heat can be dissipated quickly.
A connection may be taken from the junction of two resistors in series. This combination is known as a 'fixed potentiometer' or 'potential divider' because when it is connected across a source of voltage it enables any required proportion of the voltage to be obtained according to the values of the two resistors. These are generally fairly high in value to avoid putting too heavy a load on the source. The two resistors are often replaced by a single resistor in which the position of the 'tap' is varied by a sliding contact (a 'variable potentiometer').
The main application of the resistor in electronic circuits is to create a given voltage drop across it for a particular purpose as a result of a known current flowing through the resistor (by Ohm's Law). A fairly high value of resistor may often be employed to provide a leakage path to earth from a particular part of the circuit. Resistors are also used as the load across which the output of an amplifier stage is developed, or in which the output of a transmitter is dissipated.
![]() The resistor colour code calculator
The resistor colour code calculator